| HomeTurtlegraficsGPanelRobotics WebTigerPython |
| Python - Online |
| Deutsch English |
7. BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATION
![]()
YOU LEARN HERE... |
how two computers exchange information with each other via Bluetooth. |
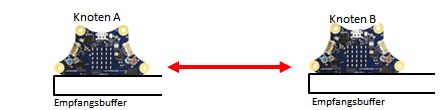
WIRELESS COMMUNICATION |
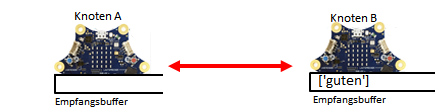
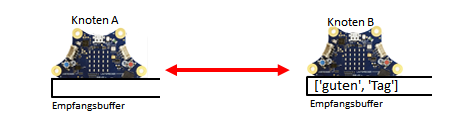
| In communication between two Calliope (also called nodes), each node is both a transmitter and a receiver. First, both nodes switch on the transmitter/receiver device with radio.on(). This creates a wireless Bluetooth connection. Subsequently, each of the nodes can send a message (as a string) to the other node with radio.send(msg), which is first stored there in a receive buffer like in a queue. With radio.receive() you fetch the “oldest” message, which is then deleted from the buffer.
|
EXAMPLES |
|
You create a wireless communication with another person to exchange information with dots and dashes (as in Morse code ). If you click on button A on one Calliope, the middle LED of the display on the other Calliope lights up for ½ s (like a dot), if you click on button B, three LEDs light up (like a dash).
The central part of the program consists of an infinite loop in which first sending and then receiving is controlled. If A is clicked, you transmit the message “p” (short for “point”), if B is clicked, you transmit “d” (short for “dash”). Then use receive() to get the oldest entry in the queue. (If this is empty, you get the special value None.) Depending on whether you have received “p” or “d”, you execute the corresponding action. Program: import radio from calliope_mini import * point = Image('00000:00000:00900:00000:00000') dash = Image('00000:00000:09990:00000:00000') def draw(img): display.show(img) sleep(500) display.clear() sleep(500) radio.on() while True: if button_a.was_pressed(): radio.send("p") elif button_b.was_pressed(): radio.send("d") rec = radio.receive() if rec != None: if rec == "p": draw(point) elif rec == "d": draw(dash) sleep(10) Real Morse stations almost always work with short and long tones. Your program should switch on the sound at the receiver as long as button A is pressed. To do this, you send the message “d” (for “down”) to the receiver when the button is pressed. When you release the button, you send “u” (for “up”). To do this, you must introduce a Boolean variable down, which you use to remember whether the button is pressed or released. Program: import radio from calliope_mini import * import music radio.on() down = False while True: if button_a.is_pressed() and not down: down = True radio.send("d") elif not button_a.is_pressed() and down: down = False radio.send("u") rec = radio.receive() if rec != None: if rec == "d": music.pitch(500, 1000000, wait = False) elif rec == "u": music.stop() sleep(10) |
REMEMBER ... |
| that the sender sends a message with send(msg), which is then stored in the receive buffer in sequence until the receiver picks up the “oldest” message in the buffer with msg = receive(). |
TO SOLVE BY YOURSELF |
|
![]()
Warning: include(a/7-1.html): Failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 221
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'a/7-1.html' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/local/lib/php') in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 221
Warning: include(a/7-2.html): Failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 225
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'a/7-2.html' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/local/lib/php') in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 225
Warning: include(a/7-3.html): Failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 229
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'a/7-3.html' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/local/lib/php') in /var/www/html/engl/robotik/cp/bluetooth.inc.php on line 229