| HomeTurtlegraficsGPanelRoboticsGameGrid WebTigerPython |
| Python - Online |
| Deutsch English |
SIMULATIONS
![]()
SWARM SIMULATION |
In your programme, you determine the neighbouring nodes by selecting those from the four adjacent cells that are not on the wall and not outside the grid. A bird in a flock wants to be close to its neighbours, but also wants to avoid collisions. Its behaviour can be described by the following rules: 1. Separation: Each actor maintains a certain distance from its neighbours to avoid possible collisions. The actor's acceleration vector is opposite to the vector of the sum of the positions of its neighbours. 2. Aligment: aims to match the speed and direction to the movement of the neighbours. The speed vector of the actor is formed as the mean value of the speed vectors of the neighbours. 3. Cohesion: aims to keep the swarm together and allows the actor to remain as close as possible to its neighbours. The direction of the actor's acceleration vector points towards the common centre of gravity of the neighbours' point masses. Program: # Swarm.py from gamegrid import * import math import random class Tree(Actor): def __init__(self): Actor.__init__(self, "sprites/tree1.png") class Bird(Actor): def __init__(self): Actor.__init__(self, True, "sprites/arrow1.png") self.r = GGVector(0, 0) # Position self.v = GGVector(0, 0) # Velocity self.a = GGVector(0, 0) # Acceleration # Called when actor is added to gamegrid def reset(self): self.r.x=self.getX() self.r.y=self.getY() self.v.x=startVelocity*math.cos(math.radians(self.getDirection())) self.v.y=startVelocity*math.sin(math.radians(self.getDirection())) # ----------- cohesion --------------- def cohesion(self, distance): return self.getCenterOfMass(distance).sub(self.r) # ----------- alignment -------------- def alignment(self, distance): align = self.getAverageVelocity(distance) align = align.sub(self.v) return align # ----------- separation ------------- def separation(self, distance): repulse = GGVector() # ------ from birds ------ for p in birdPositions: dist = p.sub(self.r) d = dist.magnitude() if d < distance and d != 0: repulse = repulse.add(dist.mult((d-distance)/d)) # ------ from trees ------ trees = self.gameGrid.getActors(Tree) for actor in trees: p = GGVector(actor.getX(), actor.getY()) dist = p.sub(self.r) d = dist.magnitude() if d < distance and d != 0: repulse = repulse.add(dist.mult((d-distance)/d)) return repulse # ----------- wall interaction ------- def wallInteraction(self): width = self.gameGrid.getWidth() height = self.gameGrid.getHeight() acc = GGVector() if self.r.x < wallDist: distFactor = (wallDist - self.r.x) / wallDist acc = GGVector(wallWeight * distFactor, 0) if width - self.r.x < wallDist: distFactor = ((width - self.r.x)-wallDist)/wallDist acc = GGVector(wallWeight * distFactor, 0) if self.r.y < wallDist: distFactor = (wallDist - self.r.y) / wallDist acc = GGVector(0, wallWeight * distFactor) if height - self.r.y < wallDist: distFactor = ((height - self.r.y)-wallDist)/wallDist acc = GGVector(0, wallWeight * distFactor) return acc def getPosition(self): return self.r def getVelocity(self): return self.v def getCenterOfMass(self, distance): center = GGVector() sum = 0 for p in birdPositions: dist = p.sub(self.r) d = dist.magnitude() if d < distance: center = center.add(p) sum += 1 if sum != 0: return center.mult(1.0/sum) else: return center def getAverageVelocity(self, distance): avg = GGVector() sum = 0 for i in range(len(birdPositions)): p = birdPositions[i] if (self.r.x - p.x)*(self.r.x-p.x) + \ (self.r.y - p.y)*(self.r.y-p.y)<distance*distance: avg = avg.add(birdVelocities[i]); sum += 1 return avg.mult(1.0/sum) def limitSpeed(self): m = self.v.magnitude() if m < minSpeed: self.v = self.v.mult(minSpeed / m) if m > maxSpeed: self.v = self.v.mult(minSpeed / m) def setAcceleration(self): self.a = self.cohesion(cohDist).mult(cohWeight) self.a = self.a.add(self.separation(sepDist).mult(sepWeight)) self.a = self.a.add(self.alignment(aligDist).mult(aligWeight)) self.a = self.a.add(self.wallInteraction()) def act(self): self.setAcceleration() self.v = self.v.add(self.a) # new velocity self.limitSpeed() self.r = self.r.add(self.v) # new position self.setDirection(int(math.degrees(self.v.getDirection()))) self.setLocation(Location(int(self.r.x), int(self.r.y))) # global section def populateTrees(number): blockSize = 70 treesPerBlock = 10 for block in range(number // treesPerBlock): x = getRandomNumber(800 // blockSize) * blockSize y = getRandomNumber(600 // blockSize) * blockSize for t in range(treesPerBlock): dx = getRandomNumber(blockSize) dy = getRandomNumber(blockSize) addActor(Tree(), Location(x + dx, y + dy)) def generateBirds(number): for i in range(number): addActorNoRefresh(Bird(), getRandomLocation(), getRandomDirection()) onAct() # Initialize birdPositions, birdVelocities def onAct(): global birdPositions, birdVelocities # Update bird positions and velocities birdPositions = [] birdVelocities = [] for b in getActors(Bird): birdPositions.append(b.getPosition()) birdVelocities.append(b.getVelocity()) def getRandomNumber(limit): return random.randint(0, limit-1) # coupling constants cohDist = 100 cohWeight = 0.01 aligDist = 30 aligWeight = 1 sepDist = 30 sepWeight = 0.2 wallDist = 20 wallWeight = 2 maxSpeed = 20 minSpeed = 10 startVelocity = 10 numberTrees = 100 numberBirds = 50 birdPositions = [] birdVelocities = [] makeGameGrid(800, 600, 1, False) registerAct(onAct) setSimulationPeriod(10) setBgColor(Color.blue) setTitle("Swarm Simulation") show() populateTrees(numberTrees) generateBirds(numberBirds) doRun() |
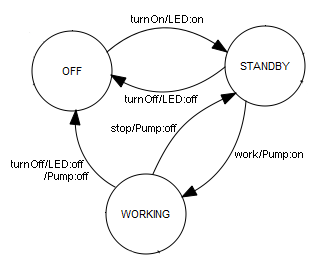
ESPRESSO AUTOMAT |
| In everyday life, you encounter many devices and machines that can be considered automatic machines. These include beverage vending machines, washing machines, cash machines, etc. As an engineer and computer scientist, you develop such a machine with the clear idea that it will gradually transition from its current state to a subsequent state, depending on sensor data and the operation of buttons and switches. |
Program: #Espresso.py from gamegrid import * def pressEvent(e): global state loc = toLocationInGrid(e.getX(), e.getY()) if loc == Location(1, 2): # off state = "OFF" led.show(0) coffee.hide() elif loc == Location(2, 2): # on if state == "OFF": state = "STANDBY" led.show(1) elif loc == Location(4, 2): # stop if state == "WORKING": state = "STANDBY" coffee.hide() elif loc == Location(5, 2): # work if state == "STANDBY": state = "WORKING" coffee.show() setTitle("State: " + str(state)) refresh() state = "OFF" makeGameGrid(7, 11, 50, None, "sprites/espresso.png", False, mousePressed = pressEvent) show() setTitle("State: " + str(state)) led = Actor("sprites/lightout.gif", 2) addActor(led, Location(3, 3)) coffee = Actor("sprites/coffee.png") addActor(coffee, Location(3, 6)) coffee.hide() refresh() |
![]()