![]()
YOU LEARN HERE... |
how to structure your programs with named program blocks, called functions in Python. The use of functions is of great importance, because you avoid having to write the same code several times in the program (code duplication) and you can use them to break down problems into smaller, easier-to-solve sub-problems. |
EXAMPLES |
The function definition begins with the keyword def, followed by the name, a so-called parameter bracket and a colon. The commands in the function body form a program block and must therefore be indented. def square(): repeat 4: forward(100) right(90) In the main program, call the function by its name. Program:
|
REMEMBER... |
You can choose the function names pretty freely, but you must adhere to a few restrictions. Allowed are names
It is common practice to begin function names with a lowercase letter and to use lowercase notation for compound names (e.g. drawFigure). English identifiers are better because they do not contain umlauts and your programs are universally readable. |
TO SOLVE BY YOURSELF |
| 1. | Define a hexagon() function with which the Turtle draws a hexagon. Use this command to create the adjacent figure. |
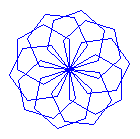 |
||
| 2. | Define a command for a square that stands on its tip and use it to draw the adjacent figure. |
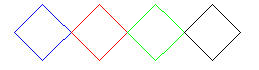 |
||
| 3a. | In the following task, you will see how you can solve a problem step by step using functions. Define a function arc() with which the turtle draws an arc and turns 90 degrees to the right. |
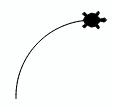 |
||
3b. |
|
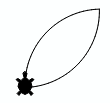 |
||
| 3c. | Extend the program with the function flower() so that an 8-petaled flower is created. |
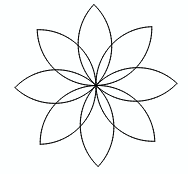 |
||
| 3d. | Extend the function blumenblatt() so that the leaves are filled with a red color
|
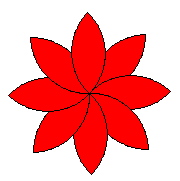 |
![]()